Are you curious about How To Tell The Gender Of A Softshell Turtle? Whether you’re a new owner determining the sex of these elusive creatures can be quite tricky. However, fear not, as we’ve got you covered!
Determining the gender of a softshell turtle usually requires an examination of its physical traits, such as the length of the tail and the shape of the plastron (bottom shell), by a trained reptile expert.

In this blog post, we’ll provide some tips and tricks on how to tell the gender of your softshell turtle with ease. So let’s dive in and unravel the secrets behind their physical features that reveal their sexes!
How To Tell The Gender Of A Softshell Turtle?
If you want to know how to tell the gender of a softshell turtle, there are some things you can look for. Males and females have different size shells and heads.
The male’s shell is usually larger and more round. The female’s shell is smaller and more oval-shaped. The male’s head is also larger, with a longer neck than the female’s. Another way to tell the gender of a softshell turtle is by looking at the plastron, or bottom shell.
The male’s plastron is concave, while the female’s plastron is flat. Males usually have brighter colours on their shells than females.
How To Determine The Gender Of A Softshell Turtle?
Determining the gender of a softshell turtle can be a bit challenging, as these reptiles do not possess easily visible external reproductive organs like mammals do. Several methods can help in identifying the gender of a softshell turtle. Let’s explore these methods:
1. Size and Weight:
In many species of softshell turtles, males tend to be smaller and lighter than females. This difference becomes more apparent as they mature. By comparing the size and weight of individual turtles, you may be able to make an educated guess about their gender.
2. Cloacal Probing:
Cloaca probing is a safe and reliable method for determining the sex of a softshell turtle. It involves inserting a blunt metal or wooden probe into the turtle’s cloaca (or opening beneath its tail).
Male turtles usually have a longer length of their reproductive organ called hemipenis. In contrast, females have only a short distance between their cloaca and an internal division called a septum.
3. Primordia-based Gender Identification:
Primordia-based gender identification involves looking at the shape and size of small bumps found on softshell turtles’ plastrons (lower shells). In male turtles, these bumps are often larger and more defined than in female turtles, which helps determine their gender.
4. Blood Test:
A blood test may also help identify the gender of your softshell turtle by checking the levels of various hormones such as testosterone or estrogen. This method requires bringing the turtle to an experienced veterinarian for testing.
5. Cloacal Examination:
A cloacal examination is similar to a cloacal probing in that it involves inserting a slender device with a light source into the turtle’s cloaca. This technique can help spot differences in the size and shape of reproductive organs between male and female softshell turtles.
6. DNA Testing:
The most accurate way to determine the gender of a softshell turtle is through DNA testing. This requires taking a sample of the turtle’s blood, tissue, or scales and sending it to a laboratory for analysis. The results will reveal whether the individual is male or female.
7. Behavior:
Observing the behaviour of a softshell turtle can also help identify its gender. Males tend to be more active and aggressive, while females show less enthusiasm for movement and display more defensive behaviour.
8. Ultrasound:
An ultrasound can be used to identify the gender of a softshell turtle. This method requires the turtle to be anaesthetized, after which an imaging device will be passed over the animal’s shells and reproductive organs. The size and shape of these organs can help determine the gender of the individual turtle.
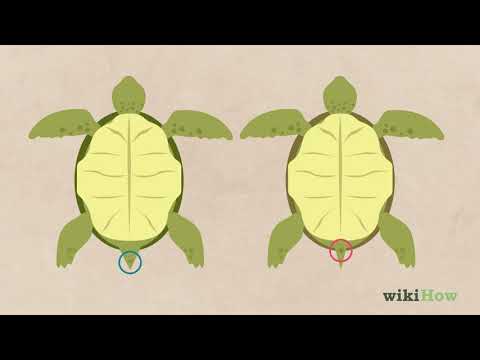
9. Vent Sexing:
Vent sexing is a technique used to determine the sex of many reptile species, including softshell turtles. This involves gently pushing the tail to one side and looking at the shape of the cloacal opening. Male turtles tend to have more angular openings, while female turtles have rounder ones.
Ultimately, the most reliable way to determine the gender of a softshell turtle is to consult an expert herpetologist or veterinarian. They will be able to properly identify the gender of your turtle through one of the methods mentioned above.
Differentiating Male and Female Softshell Turtles:
Male:
- Generally larger than females
- Longer tails
- A notch on the bottom side of their plastron (underside)
- The nuchal scutes (ridge on the neck) is more prominent
- Claws may be thicker and longer
- The vent (where waste is excreted) is further away from the tail
- Males may have a darker carapace (top/back) than females
Females:
- Generally smaller than males
- Shorter tails
- No notch on the bottom side of their plastron
- Nuchal scutes are less prominent
- Claws may be shorter and thinner
- Vent closer to the tail than in males
- Females may have a lighter carapace than males
Things You Need To Remember While Determining The Gender:
When trying to determine the gender of a softshell turtle, there are a few key things you need to remember.
- Remember that male and female turtles can vary in size, so don’t rely on size alone to make your determination.
- Look for physical characteristics that can help you tell them apart. Male turtles usually have longer tails and claws than females.
- Check for a ‘nuchal scute‘, a scute (the hard shell-like segment that makes up the turtle’s carapace) located just behind the back of the turtle’s head. This helps differentiate male from female softshell turtles.
- Look for the opening known as a ‘cloaca’ located on the turtle’s underside near its tail. This is one of the main ways to differentiate the genders. It is larger and more rounded on males than on females, who have small and pointed openings.
- If you’re unsure, you can always take your turtle to a veterinarian or herpetologist for help in determining its gender.
- Check for the size and shape of the turtle’s plastron (underside of the shell), as this can also help differentiate genders. Males typically have longer and more concave plastrons than females.
- Male turtles may also develop “nuptial scutes,” thick, raised ridges along the edge of their carapace used for mating.
- Male turtles often have brighter colours, though this isn’t a foolproof way to determine gender since female turtles can also have vibrant-coloured shells.
- Female turtles normally lay eggs, so if you notice egg-laying behaviour, your turtle is likely female.
- If you still need help, many online forums offer sexing advice from experienced turtle hobbyists and professionals who can provide advice and support in determining a turtle’s gender.
Conclusion:
There are a few things you can look for when trying to determine the gender of a softshell turtle. The best way is to look at the shape of the turtle’s shell.
Male turtles tend to have longer and narrower shells, while female turtles have shorter and wider ones. You can also look at the size of the turtle’s head.
Male turtles have larger heads, while female turtles have smaller ones. You can look at the turtle’s tail. Male turtles have longer tailed, while female turtles have shorter tails.
I hope How to Tell the Gender of a Softshell Turtle? The answer was helpful.